This web page was produced as an assignment forGenetics 677, an undergraduate course in UW Madison
HOMOLOGY
The homologues for the human GSK3B gene were obtained from Homologene database. The reason why I selected this particular set of homologues is that these are species that are well known model organisms and had been widely used in variety of experimental procedures. My goal is to compare the available published research with my findings from the different databases and establish potential areas that have not been investigated and might offer useful insights for the involvement of GSK3B in heart development.
All images retrieved from Google Images :http://images.google.com
Sequence alignments using BLAST2 Sequences
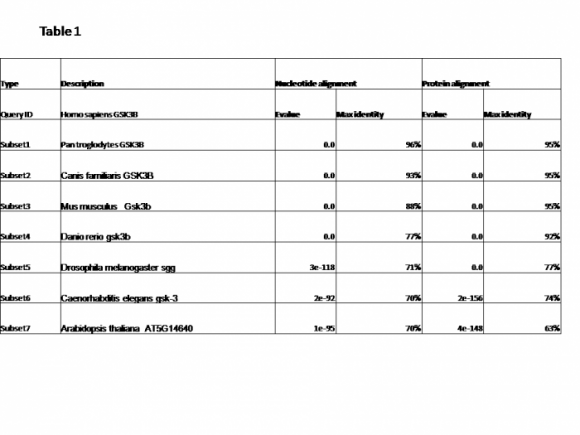
mRNA sequences were used and aligned via blastn - Homo sapiens nucleotide sequence was used as a query .At first I chose megablast program for highly similar sequences and only 3 the organisms were detected – chimpanzee(with 99% identity to the human), the dog revealed 96% identity and the mouse – 91% identity. When I changed the program to “discontiguous megablast” for more dissimilar the rest of the sequences were detected The results were summarize in Table 1 under nucleotide alignment.
Comments: Regulation on level of transcription and translation is an important aspect of many experiments. In order to identify such regulatory elements for GSKB in humans we can use model organisms such as chimpanzee, dog and mouse due to the high level of nucleotide sequence similarities between them. However lower scores in the nucleotide sequence does not necessarily mean that the coded proteins will also correlate with at the same level. To demonstrate this Blast program for pairwise alignment was performed using the protein sequence of the same organisms. Table 1 – protein alignment is a clear indication of that.
Comments: Regulation on level of transcription and translation is an important aspect of many experiments. In order to identify such regulatory elements for GSKB in humans we can use model organisms such as chimpanzee, dog and mouse due to the high level of nucleotide sequence similarities between them. However lower scores in the nucleotide sequence does not necessarily mean that the coded proteins will also correlate with at the same level. To demonstrate this Blast program for pairwise alignment was performed using the protein sequence of the same organisms. Table 1 – protein alignment is a clear indication of that.
Table 1
Conclusion
The reason why there is discrepancies between the percent of sequence similarity between the nucleotides and the protein can be explained with the fact that the general codon-anticodon code is redundant and certain sequences are more predominant in some species but not in others. However the net result – amino acid sequence remains relatively the same.
For more specific determination of which particular regions in the proteins were conserved T-coffee alignment using the protein sequence was performed. According to it there is high degree of similarities in the proteins in the different species and especially the domains that spans between the 80th and 360th amino acid residue is highly conserved in the evolution. Therefore it will be logically to expect that its biological function, the cellular localization and even the substrates it will affect will be similar. We can furthermore take a closer look at the specifics of the protein domain and the predicted functions that it has.
For more specific determination of which particular regions in the proteins were conserved T-coffee alignment using the protein sequence was performed. According to it there is high degree of similarities in the proteins in the different species and especially the domains that spans between the 80th and 360th amino acid residue is highly conserved in the evolution. Therefore it will be logically to expect that its biological function, the cellular localization and even the substrates it will affect will be similar. We can furthermore take a closer look at the specifics of the protein domain and the predicted functions that it has.
| t-coffee_results_for_protein_alignment_gsk3b_homologues.pdf | |
| File Size: | 67 kb |
| File Type: | |
References:
1. National Center of Biotechnology information:http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
2. BLAST :http://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi
3. Homologene:http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?db=homologene
4 Phylogeny fr: http://www.phylogeny.fr